
Which Pricing Strategy Should You Pick For Your SaaS Company
Defining the best pricing strategy for your subscription management business is one of the hardest yet most important tasks. With new SaaS businesses emerging in every industry, every day, it’s not surprising that pricing strategies need to become more dynamic and flexible to meet the requirements of each industry and their targeted user consumption patterns.
Akshay G Bhat
Table of content
In this article, we’ll be discussing the most popular pricing strategies used by SaaS companies and how they are best suited for businesses with particular needs.
To fully understand the different pricing strategies and to effectively implement them for your business, you need to understand the two broad categories of pricing models and the specific sub-categories within them. Let’s take a refresher at the broad pricing models – Fixed and Pay-as-you-go.
Fixed Pricing Model
Fixed pricing is a strategy where you charge a single price for your product or service, regardless of how much the customer uses it. It’s simple, clean, and easy to understand. Customers know exactly what they’re getting, and there’s no need to worry about usage tiers or complex pricing models. The downside is that fixed pricing can sometimes be too simple, and customers may not be willing to pay the same price for a service that they only use occasionally.
Pay-As-You-Go Pricing Model
The Pay-As-You-Go pricing model is based on usage, so customers only pay for what they use. This can be a great option for SaaS companies offering subscription features since it allows customers to try out the service without making a long-term commitment. Plus, it’s easy to scale up or down as needed since usage can fluctuate over time. The downside is that customers may be reluctant to sign up for a service that could end up costing them more than they anticipate.
Both the Fixed and Pay-as-you-go pricing models can work effectively for your business, as long as you are able to customize them for your specific user needs. How do you do that? By sub-categorizing these models based on Per-unit or Tiered consumption. Here’s where we explain how each of these specific combinations of pricing models can help your business.
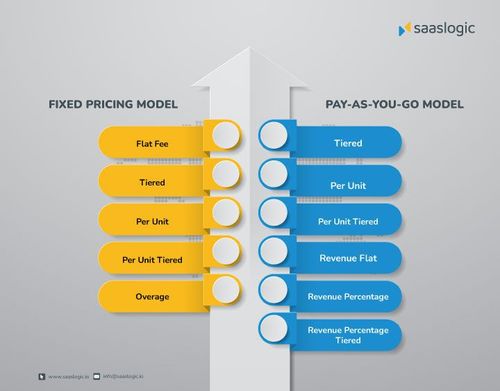
Fixed Flat Fee:- This is the simplest of all pricing models. If you are offering your SaaS product with a single set of features at a single price, this is the pricing model for you. Now you can either bill your client monthly or yearly, depending on their needs. The important thing here is that you get your price correct and make sure that it includes all costs associated with the product or service you’re offering. Flat-fee pricing is recommended for service industries such as shipping, legal services, and creative services.
Per Unit:- With per unit pricing, you set a price for each individual unit of the feature consumed. If you’re choosing a fixed pricing/pre-paid model, it means that the price of the unit remains unchanged no matter how many units are consumed. On a pay-as-you-go model, businesses could choose to set up price variations if the consumption of the unit increases beyond certain measures. This is usually a good option for products that have a high volume of consumption.
Tiered:- Tiered pricing is one of the most popular pricing strategies for software products. It involves dividing the features into different price points and offering them to different customer segments. The goal is to maximize revenue while minimizing customer churn. There are several different tiered pricing strategies. The most common type of tiered pricing is called flat pricing. Here, the price of a fixed set of features or units remains the same regardless of how much is used. This can be useful when the product or service is relatively cheap, and customers don’t want to pay for increased levels of use.
Per Unit Tiered:- The only difference between tiered flat pricing and tiered per unit pricing is that the former uses sets of features or a tier as a pricing measure and has therefore a fixed package price, whereas the latter takes into account the number of units consumed while keeping individual unit prices constant. This pricing approach, although a little more complex, helps businesses get the best value for their products.
Revenue Percentage:- Revenue percentage pricing is a pricing strategy where a product or service is priced at a percentage of the company’s revenue. For example, if a company has $1 million in revenue and wants to price its product at $100 per month, it would charge 10% of its revenue as subscription fees. Revenue percentage pricing is used to set prices that are fair for customers and manageable for the company.
Revenue Percentage Tiered:- This pricing strategy allows businesses to divide their customers into different tiers, and then charge them different prices for the same service or product. The tiers are typically based on how much revenue the customer generates for the company. For example, a company might charge different prices for its small, medium, and large customers. This strategy is often used most commonly by SaaS companies offering subscription services.
Overage Charging:- The concept of overage charges has been developed specifically for the fixed pricing/pre-paid models where there the actual units consumed differ from what was initially charged for. To compute the overage charges, businesses will check the parameter usage values in the previous billing cycle to see if they have exceeded the upper limit. If the search yields positive consumption values, the additional amount is added to the newly generated invoice for the next billing cycle.
Picking The Right Pricing Strategy For Your SaaS Business
Businesses that offer SaaS products face a unique pricing challenge. Unlike traditional products, which can be sold in a fixed price format, SaaS products typically have variable pricing. This means that the price of a subscription or service can change over time, based on demand and other factors.
The right pricing strategy for a SaaS business is key to success. It’s important to understand how different pricing models work and which one is best for your company. Thankfully, subscription management platforms like saaslogic can help them navigate these tricky waters. Our platform, for instance, can understand your company’s unique product nature, compute its costing vs revenue projections, understand previous user consumption patterns, and suggest pricing strategies that can give you the best value for your product. Good pricing packages are as essential to retaining your customers as product features or user experience.

Akshay G Bhat
Technical Content Writer
Akshay G Bhat is a Content Writer at Saaslogic, bringing over 5 years of combined expertise in both software development and technical writing. With hands-on experience in coding as well as content creation, he bridges the gap between technical depth and clear communication. His work spans blogs, SEO-driven web content, articles, newsletters, product documentation, video scripts, use cases, and more. Akshay’s unique mix of development knowledge and writing skills allows him to simplify complex concepts while delivering content that is both engaging and impactful.
Related Topics
- Why Flat Pricing Fails for AI Products: A Deep Dive into AI SaaS Pricing Models Sun Mar 01 2026
- Token-Based Pricing vs Subscription Pricing: Which Works Better for AI SaaS? Mon Feb 23 2026
- How Outcome-Based Pricing Boosts ROI for AI-Powered SaaSMon Dec 15 2025
- The Role of Machine Learning in Optimizing SaaS Revenue ModelsTue Nov 04 2025
- Dynamic Pricing in SaaS: How AI is Reshaping Subscription Revenue ModelsFri Oct 03 2025
Categories
- Churn Reduction and Customer Retention
- Pricing Strategies and Revenue Models
- Billing, Payments and Invoicing
- Customization and Enterprise Use Cases
- Growth Scale and Business Strategy
- Subscription Management and Optimization
- Technology and Integrations
- Startups and Marketing
- Trends and Thought Leadership
- SaaS Accounting & Compliance